OVERVIEW
Lag time in the production pipeline of a digital marketing company was reduced by 47.34% after introducing autonomous, AI-enabled, productivity optimization software. Over the seven-month study period, results continued to improve, indicating that new habits had been formed.
THE PROBLEM
As part of an internal workplace communication system of a digital marketing company, team members send messages to one another, inquiring after essential information. Often these inquiries require timely feedback (e.g. “What is the password?”), without which, will delay production.
Getting timely feedback from the recipient is important for several reasons, but in particular due to the introduction of lag time into the production pipeline when feedback is not provided quickly. To address this issue, the impact of an autonomous intervention system ‘MOE’, on worker response times, was tested.
THE EXPERIMENT
A digital marketing company enlisted over 50 workers to participate in a study to evaluate the impact of an autonomous intervention system, on response times.
An end-to-end autonomous system (Inspira’s ‘Machine Suite‘) was introduced on February 18th, 2023. The system included autonomous monitoring, assessment, and message-triggering by various components of the ‘machine’, Messaging to users was handled by MOE (metrics optimization engine). Data on response times was logged for seven months, providing insight into cross-sectional as well as longitudinal impact.
Autonomous interventions were designed to elicit confirmation of implementation intentions. Employees had previously committed to timely response to feedback requests, thus ‘intention’ was well established. The interventions consisted of messages reminding the recipient of the need to provide rapid feedback. Included in the message was a digital response mechanism where the user was nudged to confirm their intention, in essence, doubling-down on their previous commitment. Messages were delivered over email as well as by push notification via the company’s proprietary desktop software. The interventions were triggered via Robotic Process Automation (RPA) when the request for feedback was between 36-48 hours old, then again when it was between 48.01-60 hours old, then again when it was between 60.01-80 hours old, with a final intervention when it was more than 80 hours old.
Each subsequent message escalated in its tone of urgency.
- URGENCY 1 (36-48 hours): “Stale feedback request(s) need your attention. Can you take care of these in the next hour?”
- URGENCY 2 (48.01-60 hours): “Your stale feedback requests are getting urgent. Can you take care of these now?”
- URGENCY 3 (60.01-80): “Your stale feedback requests are getting very late!! Can you take care of these now?”
- URGENCY 4 (80+ hours): “Your stale feedback requests are causing problems… Can you sign in and check your messages now?”
Each message included a “yes” or “no” option for the participant to confirm their intention to provide feedback.
The RESULTS
Prior to the experiment (January 1st – February 17th), the average response time was 45.10 hours. During the final half of the study period (3.5 months), the average response time had dropped by 33.7% to 29.87 hours. And by the final week of the experiment, the average response time had dropped to 23.75 hours – a 47.34% reduction. (23.75 – 45.10) / 45.10 * 100 = 47.34%
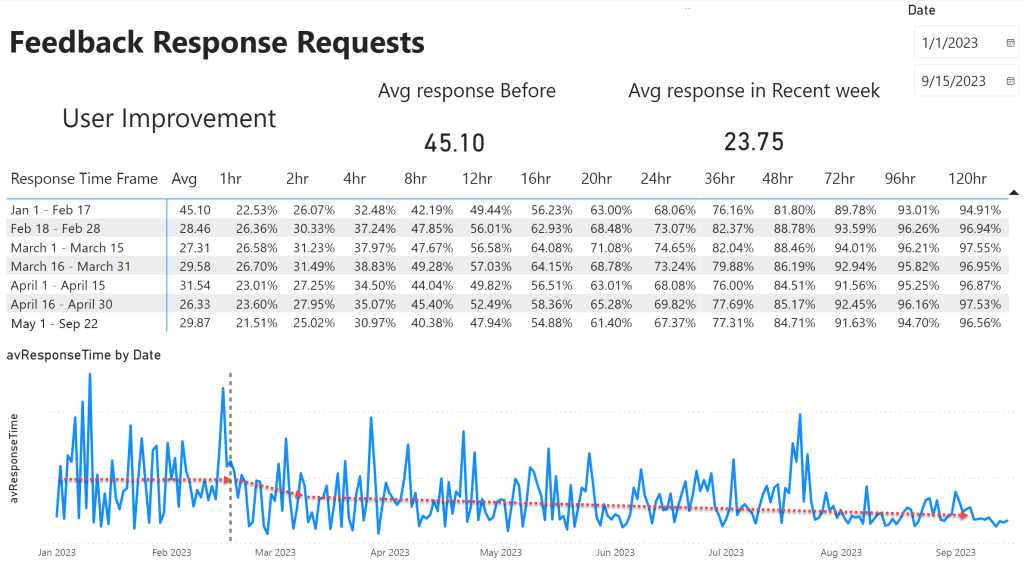
Noticeable improvements were achieved within just two weeks of introducing the autonomous system, with much slower gains thereafter. Also notable is that workers did not habituate to the intervention over time. Instead, the intervention had an increasingly positive impact as time went on, suggesting the automated intervention has lasting benefits.
Users self-reported that the messages from MOE raised their anxiety. This is particularly compelling when considering the average response time over the 2nd half of the study period (29.87 hours) was below the trigger point of the initial intervention (36-48 hours old), meaning that users appeared to have changed their habits and formed new ones in order to avoid the interventions altogether.
SUMMARY
Timely feedback on team discussions is critical to facilitate company workflow and efficiency. The results of the current study suggest that autonomous interventions can substantially reduce response times. Additionally, users spontaneously reported they noticed lower lag times in the production pipeline during the study. Overall, autonomous interventions, when combined with a request for the user to confirm their intentions, can be used to improve response times in a genuine workplace environment.

